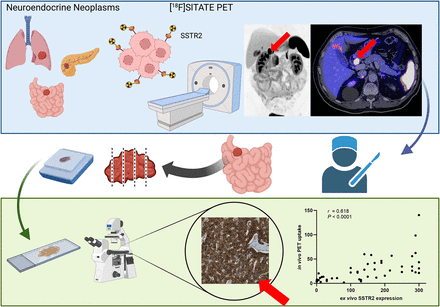
Visual Abstract
Abstract
Radiolabeled somatostatin analogs (SSAs), such as [68Ga]Ga-DOTA SSAs, have transformed imaging and therapeutic strategies. However, their use is constrained by the high cost of generators and their short half-life. In contrast, [18F]SITATE presents a promising alternative, offering the advantage of a longer half-life than 68Ga, along with the cost-effectiveness of cyclotron-based production. This study evaluated the first histologic ex vivo validation of [18F]SITATE. Methods: This study retrospectively included 47 patients (57% male; mean age, 66.9 ± 14.9 y) with histologically confirmed well-differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasms who underwent [18F]SITATE PET followed by surgery within 4 mo. Lesion uptake was quantified using SUVmean, SUVpeak, SUVmax, and tumor-to-liver ratio (TLR). Histologic somatostatin receptor (SSTR) type 2 expression was determined using histological scores (H-scores), with thresholds defining SSTR scores 1–3. The accuracy of PET imaging for preoperative metastatic detection was evaluated against surgical histology. Results: PET imaging demonstrated a significant correlation between [18F]SITATE uptake (SUVmean and TLR) and SSTR type 2 H-scores (r = 0.618 and 0.622, respectively; P < 0.0001). SSTR score 3 correlated with increased SUVmean and TLR (P < 0.0001). Among 35 patients with primary resection and lymphadenectomy, PET achieved a sensitivity of 73.9% and specificity of 100%. Conclusion: [18F]SITATE PET imaging strongly correlates with histologic SSTR expression, demonstrating utility in staging and guiding therapeutic decisions in neuroendocrine neoplasms. This 18F-labeled tracer shows specificity comparable to historical [68Ga]Ga-DOTA SSA data, whereas an increase in sensitivity for the detection of locoregional metastases appears possible. Further head-to-head comparisons of [18F]SITATE with traditional [68Ga]Ga-DOTA SSA and histologic validation are warranted to optimize its diagnostic accuracy and clinical impact.
Footnotes
↵* Contributed equally to this work.
Published online May 22, 2025.
- © 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
SNMMI members
Login to the site using your SNMMI member credentials
Individuals
Login as an individual user