Abstract
241927
Introduction: Reliable and automatic lesion segmentation adds quality to the exploration of prognostic image-based biomarkers by reducing delineation time and inter/intra-observer variability. We investigated the performance of an automatic lesion segmentation tool based on deep learning (LION, Medical University of Vienna, Austria) to segment lesions on whole-body [18F]FDG-PET/CT images of lung cancer patients.
Methods: LION has been trained using an open-source dataset (autoPET challenge) comprising more than 1,000 [18F]FDG-PET studies of patients with malignant melanoma, lymphoma, or lung cancer, and of control subjects without any cancer (). We tested LION on an independent database of baseline [18F]FDG-PET/CT images from patients with advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) subsequently treated with immunotherapy in our institution. The reference segmentation was performed manually by an experienced nuclear medicine physician (expert). To refine lesion delineation and ensure comparability between segmentations, we applied a threshold of 4 SUV to the segmentations produced both by LION (called LION4) and by the expert. The Dice score (DSC) was calculated for each patient. Two PET biomarkers were derived from the segmentations using LIFEx v.7.4.2 [Nioche et al. Cancer Res. 2018]: Total Metabolic Tumour Volume (TMTV) and Maximum Distance between two lesions (Dmax). Bland-Altman analyses were performed to characterize the differences in TMTV and Dmax between the two segmentations. The ability of features to stratify patients according to Overall Survival (OS) was compared using a Kaplan-Meier analysis. Patients were stratified in 2 groups using a cut-off value that maximized the log-rank test statistic for OS.
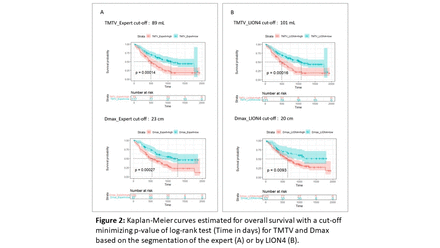
Results: A total of 196 patients were included in this study. LION segmentation yielded a mean (±1 sd) DSC of 0.5±0.2 (range: [0.0-0.9], Figure 1) across all patients before applying a threshold of 4 SUV. The mean DSC increased to 0.9±0.1 ([0.3-1.0]) after thresholding, with 82% of patients with DSC higher than 0.9. The Bland-Altman analysis showed that TMTV and Dmax measured from LION4 tended to be larger than those from the expert with a mean difference equal to 9±36 mL (Figure 1) and 5±14 cm respectively. Visual inspection showed that in cases of disagreement, LION4 had either incorrectly included regions with atypical physiological uptake, or omitted tumor regions with an uptake higher than 4 SUV. TMTV and Dmax extracted from the LION4 segmentations could both distinguish two survival profiles in patients (log-rank test: p<0.001, Figure 2). Results were similar to those obtained with the expert segmentations. Median survivals were the same between the expert and LION4 for TMTV in low- and high-risk groups (low-risk: 1082 days (d), high-risk: 489 d) and were close for Dmax (low-risk: 1286 d for the expert vs not reached for LION4; high-risk: 535 d vs 650 d respectively).
Conclusions: Automated lesion segmentation such as that provided by LION has the potential to improve inter and intra-reader reproducibility as evidenced by equivalent TMTV and Dmax values compared to the expert segmentation for lung cancer patients. Nonetheless, further training of the algorithm is ongoing to help reduce the differences still observed when comparing with expert segmentation.