Abstract
P119
Introduction: Soft tissue sarcomas are rare heterogenous tumors of mesenchymal origin. While surgical resection remains the mainstay treatment, radiation therapy often used pre or post-surgery has shown to decrease local recurrence rate. Accurate delineation of gross tumor volume is a critical step in radiotherapy planning. However, it is observer dependent, hence susceptible to both intra and inter-observer variabilities. Typically, CT and MR scans are performed including T1, T2 and contrast enhanced T1 weighted images. FDG-PET/CT is performed for staging purposes and rarely used for gross tumor volume (GTV) delineation. In this abstract we assess the effect of including FDG-PET/CT in the radiotheraphy planning of soft tisse sarcomas. We hypothesize that adding FDG PET/CT would decrease both intra and inter-observer variabilities.
Methods: A total of 61 patients with soft tissue sarcomas were included. All patients had CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT images acquired within a 4-week window period. Three trained physicians (observers) performed GTV delineation of soft tissue sarcomas using first CT and MR images only. Observers then performed GTV delineation using CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT images. Each observer performed three delineations per patient in a randomized order with at least one-month interval between trials.
DICE score and Hausdorff distance (HD) were used to assess both intra and inter-observer variabilities. For intraobserver variability, we plotted each GTV delineation drawn by each observer against its corresponding STAPLE reference for modality group. For each observer, we calculated one STAPLE per patient over the three trials drawn by the same observer. For interobserver variability, each trial was studied separately. For each trial, we calculated the DICE score between each contour drawn by the three reader and its corresponding STAPLE. For each patient, we calculated one STAPLE per trial over the contours drawn by the three observers.
The DICE scores and Hausdorff distance obtained on CT and MR images were compared to the ones obtained from CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT images. Statistical analysis was performed using a Wilcoxon signed-ranked test. A one-sided p-value of 0.025 was used as a threshold for statistical significance.
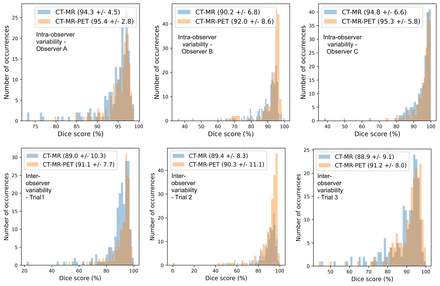
Results: For intraobserver variability, observer A had a DICE score of 90.3 when using CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT images vs. 89.3 when using CT and MR images only (p-value = 0.0018). Observers B and C had a DICE score of 92 and 95.3 when using CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT images vs. 90.2 and 94.8 respectively when using CT and MR images only (p-value < 0.0001 and p-value = 0.0022 respectively). Similarly, Hausdorff distances on CT, MR and PET images were significantly smaller for all observers. HD on CT, MR and PET measured 8.6mm, 5.7mm and 4mm vs. 9.1mm, 7.9mm and 5mm on CT and MR for observers A, B and C respectively (p-value = 0.015, p-value <0.001, p-value = 0.0003 respectively).
For interobserver variability, there is a statistically significant increase in the DICE score in all three trials when using CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT vs. CT and MR only. For trial one, the DICE score was 91.1 on CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT vs. 89 on CT and MR only (p-value = 0.0004). The DICE score was 90.3 on CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT vs. 89.3 on CT and MR only (p-value = 0.0052) and 91.1 on CT, MR and FDG-PET/CT vs. 88.8 on CT and MR only (p-value = 0.0002) for trial 2 and 3 respectively. Equally, all measured HD on CT, MR and PET images were significantly smaller across all trials. HD on CT, MR and PET was 7.7mm, 8.6mm and 7.1mm vs. 10.1mm, 9.2mm and 9.3mm on CT and MR for trials 1, 2 and 3 respectively (p-value < 0.001, p-value = 0.0017, p-value < 0.001 respectively).
Conclusions: The incorporation of FDG-PET/CT to CT and MR for the GTV delineation of soft tissue sarcomas significantly decreased both intra and interobserver variabilities.
Research support:
TR32EB013180;R01CA165221;P41EB022544