Abstract
168
Objectives: Our goal is to reduce systematic inter-scanner PET image variability. In spite of standardized protocols for scanner calibration, normalization, attenuation/scatter/randoms corrections, and image reconstruction, there exist differences in the scans acquired on different PET scanner models. These differences may manifest in the form of bias in gray-to-white, midline-to-lateral, anterior-to-posterior or superior-to-inferior ratios in addition to differences in image resolution. It is important to minimize these differences before pooling data in multi-center trials.
Methods: This work is part of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) in which FDG-PET scans of a Hoffman brain phantom were acquired at over 50 sites. All image sets were registered to a digital Hoffman phantom, producing images with a standard orientation and uniform voxel size. Scans obtained from sites having the same scanner model were reconstructed identically, normalized and averaged to obtain a single image volume per scanner model (9 models to date). We treat this as an image restoration problem and model a PET scan as a distorted form of the digital phantom (gold standard): Y ≈ a1(k)X(k) + a2(k). (Eq. 1) X(k) is the scanned phantom image from the k'th scanner model and Y is the digital phantom smoothed to match the resolution of the highest resolution scanner. a1(k) and a2(k) are restoration terms and are chosen as second order polynomials in three dimensions. Their coefficients are estimated by linear least squares fitting of Eq. 1. The corrected image is expressed as: X(corrected)(k) = â1(k)X(k) + â2(k). (Eq. 2)
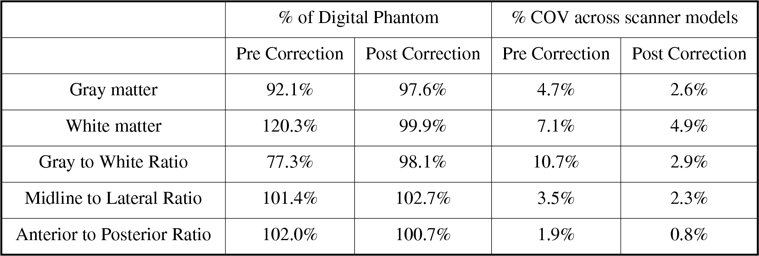
Results: Corrected images were produced for each scanner model. A set of 54 VOIs was applied to each image volume pre- and post-correction. The correction method removed nearly all the bias present in the gray and white matter regions and reduced the variability in various ratios (G:W, M:L, A:P) across the scanner models (see Table).
Conclusions: The method successfully reduced inter-scanner variability and is a good first-order correction for PET images acquired within a multi-center study.
Research Support (if any): NIH Grant: U01 AG024904
- Society of Nuclear Medicine, Inc.






