Abstract
The aim of this study was to compare the grading and prognostic value of l-[methyl-11C]-methionine (11C-MET) PET in glioma patients with 18F-FDG PET and contrast-enhanced MRI. Methods: Patients (n = 102) with histopathologically confirmed gliomas were followed up for an average of 34.6 ± 3.8 mo after PET. The median survival was 18 ± 4.7 mo in the high-grade glioma group and 58 ± 27 mo in the low-grade glioma group. Patients underwent 18F-FDG PET, 11C-MET PET, and MRI in the diagnostic and preoperative stage. The ratio of the mean standardized uptake value in the tumor to mean standardized uptake value in contralateral normal cortex (T/N ratio) was calculated. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and ANOVA were performed. Results: T/N ratios for 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET were significantly higher in high-grade gliomas than in low-grade gliomas (2.15 ± 0.77 vs. 1.56 ± 0.74, P < 0.001, and 0.85 ± 0.61 vs. 0.63 ± 0.37, P < 0.01, respectively). Median survival was 19 ± 5.4 mo in patients with a T/N ratio greater than 1.51 for 11C-MET PET and 58 ± 26.7 mo in those with a T/N ratio less than 1.51 (P = 0.03). Among the LGGs, median survival was lower in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 1.51 for 11C-MET PET (16 ± 10 mo; 95% confidence interval, 1–36 mo) than in those with a T/N ratio less than 1.51 (P = 0.04). No significant difference in survival in LGGs was based on 18F-FDG uptake and MRI contrast enhancement. Conclusion: 11C-MET PET can predict prognosis in gliomas and is better than 18F-FDG PET and MRI in predicting survival in LGGs.
Gliomas and other primary malignant central nervous system tumors comprise 1.3% of all malignancies and account for 2.3% of all cancer-related deaths (1). According to the classification of the World Health Organization (2), gliomas are categorized as of low grade and high grade; these groups are further subclassified as grades 1 and 2 for low-grade gliomas (LGGs) and grades 3 and 4 for high-grade gliomas (HGGs). Among central nervous system gliomas, glioblastoma multiforme (grade 4 astrocytoma) is the most aggressive tumor with the worst prognosis (3). Conventionally, the degree of cellular proliferation and presence of necrosis on histopathologic examination have been considered as markers of tumor grade (2). However, histopathologic examinations may suffer from sampling error and cannot be repeated frequently because of their invasive nature. Additionally, tumors located in eloquent brain regions cannot be safely biopsied. Therefore, there is a need for noninvasive methods for grading and prognosticating gliomas that can provide a global evaluation of the central nervous system lesion that does not suffer from sampling error.
Contrast enhancement on MRI is considered an indicator of tumor grade and is a commonly used clinical parameter (4). However, these findings are not specific and tumors sometimes cannot be distinguished from demyelinating lesions and abscesses. Within the category of tumors, contrast enhancement or lack of contrast enhancement can be misleading. For example, about 30% of HGGs do not enhance with contrast. Ancillary imaging techniques such as perfusion MRI and mass spectroscopy can be helpful but have their limitations.
PET provides an in vivo metabolic and functional map of intact biologic systems (5). PET has been used for several neurologic, cardiac, and oncologic indications and is currently revolutionizing clinical management in oncology (6). 18F-FDG PET has been used in the management of brain tumors for diagnosis and prognostication and has been shown to have additional prognostic significance beyond histopathologic grading (7–9). However, 18F-FDG has high uptake in normal brain cortex and low uptake in LGGs, limiting its usefulness in tumor visualization, delineation, and treatment planning (7,10). On the other hand, l-[methyl-11C]-methionine (11C-MET) is an amino acid tracer found to be useful in oncologic applications (11,12). 11C-MET has a high degree of uptake in neoplastic tissue due to its role in protein synthesis (11,12) and in transamination and transmethylation reactions (13) and increased use of amino acids for energy production and as precursors of nonproteins such as DNA, RNA, and lipids (12,14,15). 11C-MET has an advantage for imaging gliomas because, unlike 18F-FDG, it has low normal cortical uptake and high uptake in LGGs, enabling tumor visualization and treatment planning (16,17). However, the usefulness of 11C-MET PET in grading and prognostication of gliomas has limitations (18). Because of relatively high uptake of 11C-MET in LGGs, the contrast between the 11C-MET uptake in HGGs and LGGs is not as apparent on visual examination as it often is for 18F-FDG (10). Moreover, because of a definite variance in values of semiquantitative indices across subjects, several studies with a small sample size may be underpowered to detect a statistically significant difference between the 11C-MET uptake in HGGs and LGGs and its prognostic ability.
To the best of our knowledge, no studies have performed a simultaneous comparison of the relative grading and prognostic value of 11C-MET PET, 18F-FDG PET, and contrast enhancement on MRI in patients with gliomas. Therefore, our goal was to perform such a study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between 1998 and 2006, we studied the glucose metabolism and amino acid uptake of brain tumors with 18F-FDG PET and 11C-MET PET in patients referred for evaluation of central nervous system lesions. In this retrospective study, we included patients with histologically proven brain tumors according to the criteria of the World Health Organization. The histologic diagnosis was obtained after a partial or total excision of the lesion or by stereotactic biopsy. Patients studied with PET who were followed longitudinally until death or for at least 6 mo were included in the analyses. The Institutional Review Board of Kettering Medical Center Network approved all human investigations. Patient consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board for this retrospective study.
PET Methods
Patients underwent 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET on the same day at Kettering Medical Center between 1998 and 2006 after being referred to the Nuclear Medicine Clinic in the diagnostic and preoperative stage. Patients were instructed to eat a low-protein meal 1–2 h before the 11C-MET PET scan. The patient’s head was placed in the gantry and secured with adhesive tape or a thermoplastic mask. A 5- to 10-min transmission scan using a 68Ge source was acquired before the administration of the radiopharmaceutical. Approximately 740 MBq (20 mCi) of 11C-methionine were injected, and dynamic scans were acquired for 40 min. The dynamic frames were then summed and coregistered with an MRI scan (usually contrast-enhanced, T1-weighted). Subsequently, an 18F-FDG study was acquired. Cerebral uptake of intravenously administered 18F-FDG (185–370 MBq [5–10 mCi]) occurred while patients lay with their eyes open in a dimly lit, quiet room. Emission scanning with a high-resolution Siemens ECAT EXACT HR+ scanner in 3-dimensional mode (Siemens-CTI PET Systems Inc.) commenced 40 min after the injection of 18F-FDG. The patients were placed in the PET camera, and contiguous transaxial slices were obtained parallel to the canthomeatal line. Images were reconstructed using a measured attenuation correction and displayed in axial, sagittal, and coronal orientations as contiguous planes of brain tissue. All patients underwent MRI before the PET studies, and in most cases, the PET images were coregistered with the MR images. Transaxial images of 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET scans were used to define the regions of interest. The diameters of the regions of interest were chosen depending on the size and aspects of the tumor on 11C-MET PET images. The slice containing the highest uptake in the tumor was selected. A close-fitting region of interest was drawn on the tumor showing maximal radiopharmaceutical uptake. This region of interest was copied and used for the contralateral normal cortex. The ratio of the mean standardized uptake value in the tumor to mean standardized uptake value in contralateral normal cortex (T/N ratio) was calculated.
Patients
Patients (n = 102; 97 adults and 5 children) with histopathologically confirmed gliomas were included in the study. The histopathologic diagnosis for the 97 adult patients (mean age ± SD, 51.2 ± 14.1 y) is given in Table 1.
Histopathologic Diagnoses in 97 Adult Patients
Patients were followed up for an average of 34.6 ± 3.8 mo after PET. Most of the pertinent information was obtained from the Kettering Medical Center medical records, including the demographic profile, clinical features, dates and findings of the CT/MRI and PET scans, and treatment protocol. Where required, the patient, patient’s caregivers, and patient’s referring or most recent managing physicians were contacted, and clinical data relating to the patient’s functional status were requested. The information on MRI contrast enhancement was obtained from the reports of these investigations obtained from the database and was available for 78 of the included patients. For 3 of these patients, information on contrast enhancement was obtained from CT data. Data pertaining to individual patients were kept confidential.
Statistical Analysis
Mean T/N values were obtained for 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET for LGGs, HGGs, and grades 1–4 gliomas. All values were reported as mean ± SD. Between-group comparisons were performed using the unpaired Student t test and using the Mann–Whitney test in the case of nonparametric data. Multiple-group comparisons were performed using 1-way ANOVA. The χ2 test was used for comparing data involving discrete outcomes. Receiver-operating-characteristic analysis was performed to compare the performance of 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET in distinguishing LGGs from HGGs at different cut-offs of T/N values. The area under the curve was calculated. Kaplan–Meier curves were obtained to compare the survival between groups based on appropriate 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET cutoff T/N values and the presence or absence of contrast enhancement on MRI. The log-rank test was used to determine the statistical significance of any observed differences in the survival between groups. A 2-tailed P value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
Grading
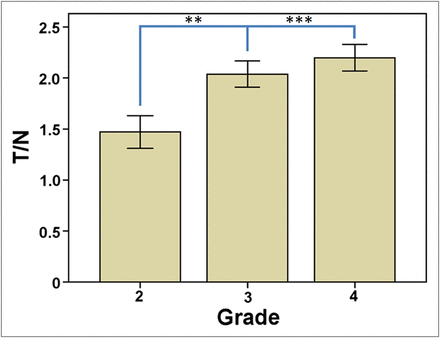
Both tracers showed an increase in T/N values with increasing grade, and this difference was statistically significant (P = 0.03). T/N ratios for 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET were significantly higher in HGGs than in LGGs (2.15 ± 0.77 vs. 1.56 ± 0.74, P < 0.001, and 0.85 ± 0.61 vs. 0.63 ± 0.37, P < 0.01, respectively). There was a statistically significant difference between T/N ratios for grade 4 and grade 2 gliomas based on 11C-MET PET (P = 0.005) and between T/N ratios for grade 4 and grade 3 (P = 0.03) and grade 4 and grade 2 gliomas (P < 0.01) based on 18F-FDG PET. When adult patients with grades 2–4 astrocytomas were analyzed separately, similar results were obtained for 11C-MET PET (Fig. 1). Overall accuracy for 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET for distinguishing HGGs and LGGs was comparable, as determined by receiver-operating-characteristic analysis (area under the curve, 0.72 and 0.66, respectively). Contrast enhancement was present in a significantly higher proportion of patients with HGGs than LGGs (90% vs. 62%, respectively, P = 0.01).
Grading value of 11C-MET PET among adult patients with grades 2–4 astrocytomas. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001.
Prognostication
Overall
The median survival was 19 ± 5.4 mo (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.2–29.73 mo) for all patients (irrespective of histologic grade of the tumor) with a mean T/N ratio greater than 1.51 for 11C-MET PET and 58 ± 26.7 mo (95% CI, 5.6–110.4 mo) for those with a mean T/N ratio less than 1.51. This difference was statistically significant (P = 0.03) (Fig. 2).
Prognostic value of 11C-MET PET (A), 18F-FDG PET (B), and MRI (C) in all patients with glioma (P = 0.03 for 11C-MET PET, 0.03 for 18F-FDG PET, and 0.26 for MRI contrast enhancement; survival in months).
Similarly, the median survival was 19 ± 4.19 mo (95% CI, 10–27.3 mo) in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 0.51 for 18F-FDG PET and was significantly lower than the median survival in those with a T/N ratio less than 0.51. This difference was also statistically significant (P = 0.03) (Fig. 2).
However, no statistically significant difference in survival was observed between patients with and without MRI contrast enhancement (P = 0.26).
LGGs
Among the LGGs, the median survival was 16 ± 10 mo (95% CI, 1–36 mo) in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 1.51 and was lower than the median survival in those with a T/N ratio less than 1.51. This difference was statistically significant (P = 0.04) (Fig. 3).
Prognostic value of 11C-MET PET (A), 18F-FDG PET (B), and MRI (C) in patients with LGGs (P = 0.04 for 11C-MET PET [P value improved to 0.02 when adults with grades 2–3 astrocytomas were analyzed separately], 0.38 for 18F-FDG PET, and 0.71 for MRI contrast enhancement; survival in months).
The median survival was 41 ± 10 mo (95% CI, 21.4–60.6 mo) in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 0.51 for 18F-FDG PET and was lower than the median survival in those with a T/N ratio less than 0.51. However, this difference did not attain statistical significance (P = 0.38) (Fig. 3). Similarly, no difference in survival was noted using MRI contrast enhancement in this group of patients (P = 0.71).
HGGs
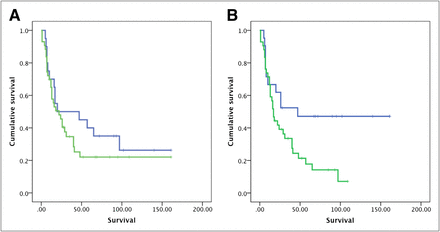
No statistically significant difference was observed in the survival duration based on T/N ratios for either 11C-MET PET or 18F-FDG PET. The median survival was 22 ± 5.5 mo (95% CI, 11.2–32.7 mo) in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 1.51 for 11C-MET PET and 16 ± 2.3 mo (95% CI, 11.5–20.5 mo) in those with a T/N ratio less than 1.51 (P = 0.78). The median survival was 17 ± 3.2 mo (95% CI, 10.6–23.4 mo) in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 0.51 for 18F-FDG PET and 25 ± 14.8 mo (95% CI, 0–55 mo) in those with a T/N ratio less than 0.51 (P = 0.21). Similarly, no difference in survival was noted using MRI contrast enhancement in this group of patients (P = 0.63) (Figs. 4A and 4B; Supplemental Fig. 1).
Prognostic value of 11C-MET PET (A) and 18F-FDG PET* (B) in patients with HGGs (P = 0.78 for 11C-MET PET and 0.21 for 18F-FDG PET; survival in months). *P value improved to 0.10 when adult patients with grades 2–4 astrocytomas were analysed separately. (Prognostic value for MRI is presented in Supplemental Fig. 1 [P = 0.63].)
Lesions With Contrast Enhancement
18F-FDG PET was predictive of survival in patients with MRI contrast enhancement. The median survival was 47 mo in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 0.51 for 18F-FDG PET and 17 mo in those with a T/N ratio less than 0.51 (P = 0.02). There was no difference in survival in these patients using 11C-MET PET (median survival, 20 vs. 22 mo, P = 0.32) (Fig. 5).
Prognostic value of 11C-MET PET (A) and 18F-FDG PET (B) in patients with contrast enhancement on MRI (P = 0.32 for 11C-MET PET and 0.02 for 18F-FDG PET [P value was 0.03 for 18F-FDG when adult patients with grades 2–4 astrocytomas were analyzed separately]; survival in months).
Lesions Without Contrast Enhancement
11C-MET PET was predictive of survival in patients without MRI contrast enhancement. The median survival of 12 mo in patients with a mean T/N ratio greater than 1.51 for 11C-MET PET was significantly lower than that in patients with a T/N ratio less than 1.51 (P = 0.05). There was no difference in survival in these patients using 18F-FDG PET (Fig. 6).
Prognostic value of 11C-MET PET (A) and 18F-FDG PET (B) in patients without contrast enhancement on MRI (P = 0.05 for 11C-MET PET and not significant for 18F-FDG PET; survival in months).
Proposed algorithm for imaging-based prognostication.
DISCUSSION
A significantly higher uptake of 11C-MET and 18F-FDG was found in HGGs than in LGGs. The differences in 11C-MET uptake between grade 4 and grade 2 gliomas and in 18F-FDG uptake between grade 4 and grade 3 gliomas and between grade 4 and grade 2 gliomas were also significant. Contrast enhancement did not predict survival in any of the univariate analyses. However, it did serve to stratify subjects for PET-based prognostication. Among the contrast-enhanced lesions, 18F-FDG PET was predictive of survival. Among the unenhanced lesions and LGGs, 11C-MET PET was predictive of survival (Fig. 7). Similar results were obtained when adult patients with grades 2–4 astrocytomas were analyzed separately.
Our findings are consistent with those of others who have demonstrated a significant difference in the 11C-MET uptake indices of low-grade and high-grade tumors (19). Similar to our results, an overlap among tumors of several grades was observed. A study of 194 patients (20) demonstrated that although the T/N ratio for 11C-MET PET (ratio of standardized uptake value in tumor to contralateral normal brain) was significantly different in the LGGs and HGGs, there was no significant difference between grades 1 and 2 gliomas or between grades 3 and 4 gliomas. Another study has reported a significant difference in the mean 11C-MET PET standardized uptake value of 1.49 ± 0.44 (mean ± SD) for grade 2 gliomas and 3.20 ± 0.92 for grade 4 gliomas (21).
Mean tumor uptake to mean contralateral gray matter uptake has been used as an index of radiotracer uptake in our study. Mean uptake values are likely to be more accurate and reliable than maximum uptake values because the latter are more sensitive to noise in the data and parameters used for image reconstruction. A similar index was used by Terakawa et al. for studying the role of 11C-MET PET in distinguishing recurrence from necrotic tumor tissue (22). Kaschten et al. (23) found this to be the most useful index. A standardization of radiotracer uptake indices is necessary for comparing results across studies.
In our study, 18F-FDG PET predicted survival in patients with enhancing lesions, and 11C-MET PET predicted survival in patients with nonenhancing lesions. Contrast enhancement reflects a breakdown of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), whereas increased 11C-MET uptake reflects an increased transport into the proliferating cells independent of the BBB. This biologic principle underlies the additional utility of 11C-MET PET over conventional imaging in the evaluation of gliomas, including grading, prognostication, tumor delineation beyond areas of contrast enhancement, and treatment planning (10). Indeed, the tumor size delineated by 11C-MET PET has been found to be larger than areas of contrast enhancement in several studies because proliferating cells extend beyond the area of BBB breakdown. Herholz et al. (16) found that 11C-MET uptake in LGGs was not affected by steroid administration, which is supposed to stabilize the BBB, implying that 11C-MET uptake is independent of BBB status in these patients. In HGGs, however, a 25% reduction in 11C-MET uptake was seen after steroid administration, implying a role for BBB breakdown in 11C-MET uptake in these patients (16). These findings could also explain why 11C-MET PET did not have prognostic ability in HGGs and contrast-enhanced lesions in our study. On the other hand, 18F-FDG uptake is a measure of viable tumor tissue and tumor malignancy manifested by an upregulation of cellular hexokinase and glucose transporters. Several of the patients with contrast enhancement actually had LGGs and thus lower uptake of 18F-FDG. Similarly, the contrast enhancement in HGGs may be partly accounted for by BBB breakdown in necrotic tumor tissue. The 18F-FDG uptake is more reflective of viable tumor tissue mass in these patients, thereby predicting survival. These factors could explain the significant prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET in patients with contrast enhancement in our study.
This ability of 18F-FDG PET and 11C-MET PET to provide additional prognostic information beyond contrast enhancement is clinically significant and calls for a randomized controlled trial to study the additional utility of 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET in patient evaluations. The difference in their prognostic value in contrast-enhanced and unenhanced lesions, respectively, highlights their complementary nature and supports our clinical practice of more than a decade of obtaining scans using both 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET in patients with suspected gliomas referred to us for evaluation. Our approach of scanning patients with both tracers on the same day is a feasible one that has been used by others and is convenient for the patients (12,17).
Our results suggest that, in addition to providing prognostic information beyond conventional imaging, 11C-MET PET provides additional prognostic information beyond histopathologic examination. Patients with LGGs who had a high uptake (T/N > 1.51) on 11C-MET PET had a poorer prognosis than those who had a lower uptake. In fact, the median survival in this group was comparable to that in the HGG group. It is possible that the high 11C-MET uptake in patients with LGGs is a result of malignant transformation over time. In that case, a significantly poorer prognosis in this group underscores the value of 11C-MET PET in assessing tumor progression. Further randomized studies are needed to assess the value of treatment based on 11C-MET PET stratification in LGG patients.
In our study, 18F-FDG PET did not demonstrate a statistically significant prognostic value in the LGGs. Most of the LGG lesions are either hypometabolic or isometabolic on 18F-FDG PET (24) but can be visualized by 11C-MET PET. The presence of statistically significant prognostic value based on 11C-MET PET in this head-to-head comparison in our study suggests that 11C-MET PET is a better tool for prognostication than 18F-FDG PET in LGG patients. Additionally, there was no evidence of the prognostic value of 11C-MET PET in the subset of HGG patients, possibly because of a high uptake of 11C-MET in lesions with tumor necrosis and BBB breakdown. Hypermethylation—one of the mechanisms responsible for 11C-MET uptake in tumor tissues (12)—may be associated with long-term survival (defined as survival > 3 y), which is observed in 3%–5% of glioblastoma patients (25).
Our study has several limitations. It is a retrospective study exploring the prognostic value of the PET modalities for overall survival. Our study population is heterogeneous, including all HGGs and LGGs without subclassification by age, histopathologic subtypes (oligodendrogliomas vs. astrocytomas), chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., 1p/19q codeletions), molecular prognostic markers (e.g., O-6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase [MGMT], isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 [IDH-1] status), and treatment (e.g., extent of resection). A head-to-head comparison of 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET in all patients serves to control for these heterogeneities and enables a valid comparison of 11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET for grading and prognosis in gliomas. Further studies are needed to incorporate 18F-FDG PET and 11C-MET PET findings in the overall prognostic schemata in glioma patients. In addition, to conclusively prove the usefulness of 11C-MET PET in clinical decision making and improving patient outcomes, prospective randomized controlled trials should be conducted, with the treatment arm consisting of patients with LGGs who are treated according to the 11C-MET PET uptake criteria as stated above and a control arm consisting of patients managed according to the conventional approach (26).
CONCLUSION
Our study suggests that 11C-MET PET can predict prognosis in glioma and is better than 18F-FDG PET and MRI in predicting survival in LGGs. Further studies are needed to incorporate 18F-FDG PET and 11C-MET PET findings in the overall prognostic schemata in glioma patients and making treatment decisions in LGG patients.
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank staff members at the Department of Nuclear Medicine/PET at the Charles F. Kettering Memorial Hospital, Kettering, Ohio, for their hard work and dedication. Part of this work was presented at Radiological Society of North America meeting held in Chicago in 2010 and was awarded the RSNA Molecular Imaging Travel Award. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Footnotes
Published online Oct. 10, 2012.
- © 2012 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Inc.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication December 28, 2011.
- Accepted for publication June 25, 2012.