Abstract
PET is an important functional imaging technique that can be used to investigate neurotransmitter receptors and transporters directly by mapping human brain function. PET is increasingly being used greatly to advance our understanding of the neurobiology and pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Methods: This review focuses on the use of PET tracers and kinetic modeling in identifying regional brain abnormalities and regions associated with cognitive functioning in schizophrenia. A variety of PET tracers have been used to identify brain abnormalities, including 11C, 15O-water, 18F-fallypride, and l-3,4-dihydroxy-6-18F-fluorophenylalanine (18F-FDOPA). Results: Some studies have used compartmental modeling to determine tracer binding kinetics. The most consistent findings show a difference in the dopamine content in the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate gyrus, and hippocampus between healthy controls and patients with schizophrenia. Studies also show a higher density of D2 receptors in the striatum and neural brain dysconnectivity. Conclusion: Future investigations integrating clinical, imaging, genetic, and cognitive aspects are warranted to gain a better understanding of the pathophysiology of this disorder.
PET is a functional neuroimaging tool. In recent years, it has been used to determine the distribution of important neurotransmitters in the human brain. Compared with other functional imaging techniques, PET enables changes in the distribution of tracer activity to be assessed qualitatively and quantitatively. In contrast, functional MRI is noisy and leads to signal distortion from nearby tissues, affecting quantitative assessment. PET has therefore been used to gain insight into neurochemical pathways (1,2). Patients with schizophrenia show heightened dopaminergic transmission leading to synaptic dysregulation (3,4), which is associated with positive symptoms (5–7). Kapur (8) suggested that this is more likely a result of presynaptic dysregulation than increased dopamine receptors. PET and SPECT use tracers that specifically bind to receptors that can be used to measure changes in receptor occupancy.
PET has provided useful insights into the pathophysiology of schizophrenia that have recently led to an upsurge in research interest. We introduce briefly the concept and basic principles of PET. Studying dopaminergic imbalances in schizophrenia requires an in-depth insight into other associated factors. We therefore provide an overview on schizophrenia. This background will prove useful as a basis for understanding subsequent sections, which discuss the use of PET to identify regional brain abnormalities in schizophrenia. We provide an integrative review of the leading ideas that use PET to detect neural activity and changes in cognitive activation paradigms.
PRINCIPLES OF PET/CT
PET facilitates the assessment of cerebral metabolic activity and blood flow and identifies the activation of dopaminergic pathways using specific tracers and neurotransmitter receptor function. These tracers emit positrons that interact with nearby electrons, producing γ-photons that are detected by scintillation crystals in the scanner, producing an image of tracer uptake.
Dopamine receptor function studies involve the injection of a radiolabeled tracer having high affinity and specificity for a specific receptor. Quantification is based on the amount of receptor binding over time. This technique can also be used to observe the effects of drugs on the binding efficiency of brain dopamine receptors. The data can also be used to determine the degree of receptor occupancy and drug uptake time, which may help determine the optimum dose. It is also possible to create a detailed map of motor function or cognitive processes of the brain while an individual is undergoing a cognitive task “online.”
OVERVIEW OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
Schizophrenia is a severe and complex brain disorder. The lifetime prevalence is around 1.4–4.6 per 1,000 and the annual incidence between 0.16 and 0.42 per 1,000 (9). It afflicts almost 1% of the world's population, is the seventh most costly medical illness in our society (10), and ranks ninth in global burden of illness (11,12). Schizophrenia typically has an onset in late adolescence or early adulthood and is characterized by positive and negative symptomatology together with defects of psychosocial and cognitive functioning (13). The clinical diagnosis is based on the DSM-IV-TR of the American Psychiatric Association (14), which requires patients to present with core symptoms for at least 1 month.
Symptoms vary over the course of the illness but broadly fall into 4 phases (premorbid, prodromal, residual, and active). The prodromal and residual phase symptoms are relatively mild forms of the active phase (Fig. 1).
Course of illness and clinical phases of schizophrenia. (Courtesy of Nora S. Vyas, PhD, 2008, Institute of Psychiatry, King's College London, U.K.)
Cognitive Deficits
Cognitive dysfunction is a recognized feature in schizophrenia. Patients perform 1.5–2.0 SDs below the normative mean of healthy age-matched individuals (15), with differential impairment in verbal learning and memory function up to 3 SDs (16–18). Neurocognitive deficits occur independently of antipsychotic treatment (17) and are not necessarily associated with psychotic symptoms (19,20). Cognitive deficits appear to be a primary predictor of functional outcome (21,22). Cognitive impairments are relatively stable across all domains (23) and do not fluctuate in accordance with clinical symptom change (16).
Neurodevelopmental and Genetic Influences
The original neurodevelopmental model proposed that disruptions in the central nervous system during ontological development (second or third trimester) interact with normal brain maturational events and may result in structural brain abnormalities that cause symptomatology (24). Recent formulations have integrated biological and environmental factors that may influence brain development during adolescence (25,26). Schizophrenia has a strong genetic predisposition, with heritability estimates of approximately 80% (27,28).
It is well established that schizophrenia has a multifactorial basis whereby the additive actions of several genes of small effect combined with the effects of noninherited factors (environmental risk indicators) contribute to increased liability to the disorder (29). Several genes associated with schizophrenia seem to have a functional role over the life span (27). Evidence from linkage studies favors disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 (30,31), neuregulin-1 (32,33), and dysbindin (34,35) as the most promising candidate genes for schizophrenia (36). Some neurochemical genes associated with dopamine regulation, such as the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene (37,38), have been associated with performance during prefrontal-mediated working memory tasks (39–43). Several genes are involved in other neurotransmitter pathways. More recently, technologic advances have shown that copy-number variants (CNVs) could be important in disease pathogenesis (44). CNVs are DNA segments (>1 kilobase) that are at the rare (e.g., 1/500 patients) end of the disease spectrum and are commonly a duplication or deletion with frequencies of more than 1%. Two CNVs have been found to be associated with increased risk: deletions at 1q21.1 and 15q13.3 (45). Higher burdens of deletions have been identified in childhood-onset schizophrenia (20%) than in adult-onset cases (15%) and healthy controls (5%) (45). Evidence suggests that several CNVs may be linked with increased susceptibility to schizophrenia. There is urgency for the replication of such findings to strengthen the evidence for the association with CNVs and schizophrenia.
NEUROCHEMICAL FINDINGS
Dopamine Hypothesis
The reformulated dopamine hypothesis suggested that striatal hypodopaminergia was associated with negative symptoms and striatal hyperdopaminergia with positive symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions, and antipsychotic treatment response (24,46). The hypothesis was driven by the discovery that all typical antipsychotic medications are dopamine receptor antagonists and that amphetamines (known dopamine-releasing agents) can induce paranoid psychotic features. Volkow et al. (47) reviewed the dopamine hypothesis.
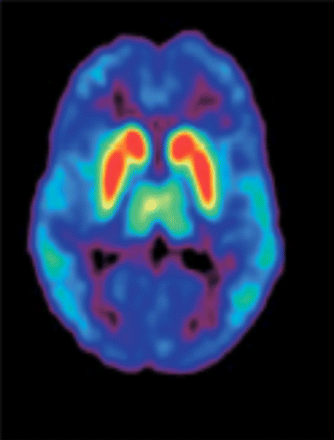
A further revision of the dopamine hypothesis, based on findings stemming from imaging studies identifying brain anatomic and connectivity abnormalities, cognitive impairments, molecular genetics, and the influence of environmental risk factors, has provided vital insights into the dopamine pathways (48). Positive symptoms are considered to be a result of the increased subcortical release of dopamine causing greater stimulation of D2 receptors (D2Rs); therefore, the primary target of many antipsychotic drugs is antagonism at striatal D2Rs. Cognitive deficits and negative symptoms are resistant to treatment by most typical antipsychotic drugs and arise from reduced D1 receptor (D1R) stimulation (49). The distribution of D2Rs in specific brain regions has been noted (Fig. 2) (50). An association of D2Rs and cognitive processes has been demonstrated.
Distribution of D2Rs in human brain (transaxial PET image using 11C-FLB 457). Colors represent amount of dopamine binding, with red as high and blue as low. High bindings are found in striatum, intermediate bindings in thalamus, and low bindings in cortex. (Reprinted with permission of (50).)
PET findings on drug-naïve schizophrenia patients have reported inconsistencies in D1R binding and cognitive functioning. Some studies have shown a decrease in prefrontal D1R binding (51), whereas others have shown an increase in D1R binding (49) or reported no differences between patients and controls (52). A few have shown a relationship between D1 dysfunction and working memory performance in medication-naïve patients. However, the findings have been inconsistent. The variability in the findings may result from the way different radioligands are metabolized.
D1Rs appear to provide a permissive role for the action of dopamine agonists on D2Rs (53). Neuronal presynaptic sites can be labeled with probes for the dopamine transporter, and the postsynaptic sites can be labeled with D1R or D2R probes, with synapses being measured by the displacement of receptor tracers by dopamine.
Kapur (8) proposed that increased dopaminergic neurotransmission is a state of dysfunction associated with positive symptomatology and suggested that during the late adolescence period patients develop abnormalities in the formation of the dopamine system that do not synchronize with normal stimuli and lead to an exaggerated release of dopamine. This has been supported by other groups (54,55).
Abi-Dargham et al. (3) measured striatal D2Rs with a D2R antagonist in 18 untreated patients and 18 controls. Previously, no difference has been seen between these 2 groups. Differences were apparent only when the participants were depleted of dopamine by 75%. The study suggests that patients with schizophrenia have a greater occupancy, and presumably simulation of D2Rs by dopamine, with patients having the most overactive dopamine system responding best to drugs. The low concentration of D2Rs in extrastriatal regions has limited the use of PET in D2 measurement.
To extend the dopamine hypothesis, Kapur et al. (56) combined the biological role of dopamine and a theory on motivational salience, whereby apparently neutral events or stimuli grab the attention because of their association with rewards and aversions (reinforcement), leading to goal-specific behavior because of striatal dopamine release (57,58). Therefore, increased dopamine release, which occurs in acute psychosis (3), leads to the assignment of increased attention and excessive reinforcement (or salience) to relatively innocuous stimuli. Delusions are then an attempt to resolve the imbued conflicting and confused state of mind (59). In the context of the development of the full-blown illness, dopamine is “the wind of the psychotic fire” (60).
Dopamine transmission is important in cognitive performance. Severe spatial working memory impairments result from prefrontal cortical dopamine depletion cortex (61). Arnsten (62) suggested an inverted-U curve relationship of D1R activation and prefrontal function, whereby excessive or insufficient dopamine levels are associated with impaired working memory performance. The administration of a D1R agonist improves performance in rats that initially showed poor attentional ability, whereas no amelioration occurs in rats with good performance (63). The administration of a D2R agonist improves cognitive abilities in humans with low basal memory but shows impairments in performance in individuals with high basal memory capacity (64). A possible explanation for changes associated with dopaminergic hypofunction or hyperfunction may be offered by the finding that those with COMT Val158 homozygosity demonstrate suboptimal prefrontal cortex (PFC) dopamine activity, whereas COMT Met158 homozygotes show an intermediate PFC dopamine state. Amphetamine treatment differentially affects the COMT Val158Met gene, whereby Val158 homozygotes show improved performance on PFC-related cognitive tasks and thus PFC efficiency. Met158 homozygotes, however, show impairments in PFC function resulting from superoptimal dopamine levels (65). Thus, prefrontal function, dopamine D1 activation, and basal activity are related (66,67).
Subsequent PET studies have shown that schizophrenia is associated with heightened presynaptic striatal dopamine synthesis and storage (68,69). The administration of amphetaminelike drugs causes an increase in striatal dopamine in schizophrenia (70,71), leading to a change in the specific binding of the D2/D3 PET ligand in drug-free and drug-naïve patients but only when patients are acutely symptomatic and not during remission. D2R densities are increased in schizophrenia, but antipsychotic treatment is a confounder (72).
5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Type 2A (5-HT2AR) and Schizophrenia: PET Studies
Serotonin (5-HT) is a neurotransmitter that occupies a unique place in neurobiology because of its role in several physiologic processes. Serotonin has been implicated in a wide range of central nervous system functions including sleep, pain reception, sexual behavior, thermoregulation, hormone secretion, appetite, and cognitive function and the modulation of responses to stress and anxiety.
Over half a century ago, the biochemists Dilworth Wayne Woolley and Elliott Shaw, who had performed seminal work on serotonin (also known as enteramine at that time), suggested that on the basis of infra-human animal laboratory studies changes in central serotonergic pathways were likely to be germane to schizophrenia and that, therefore, serotonergic pharmacologic human trials in schizophrenia were indicated (73). In addition, serotonin was initially considered to be important in schizophrenia because of the effects of atypical antipsychotics on serotonin receptors and the psychotogenic effects of LSD. Postmortem human studies have demonstrated decreased cortical 5-HT2AR in schizophrenia, although to date there are no converging data to support a particular allelic variant of this receptor as being etiologic (74). Using single-point saturation analyses to estimate the total number of 3H-ketanserin binding sites in tissue sections, Dean et al. have recently found evidence consistent with the hypothesis that apparent decreases in 5-HT2AR in schizophrenia are the result of altered levels of a regulatory factor (or factors) that modulates the binding of ligands to the 5-HT2AR; separating the membrane and cytosol removes this regulatory control (75). Furthermore, a significant interaction has been reported in schizophrenia between the Val66Met brain-derived neurotrophic factor and 5-HT2AR T102C polymorphisms and visual attention (76). On the basis of this evidence, and given the availability of suitably selective radioligands, it is clearly apposite to perform 5-HT2A PET studies in this illness (4,6). 5-HT2AR PET radiotracers with appropriate in vivo properties include 18F-setoperone (77), 18F-altanserin (78), and 11C-MDL 100 907 (79).
Trichard et al. (80) compared cortical 5-HT2AR density using 18F-setoperone PET in antipsychotic-free or antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia patients and healthy controls; no significant group difference was observed in whole or regional radiotracer cortical binding potential. Lewis et al. (81) reported similar results with 18F-setoperone PET. Verhoeff et al. (82) have criticized these studies on the grounds that the predefined regions of interest (ROIs) were observer-dependent, with much of the brain left unexplored; these authors performed a similar study, with the data being analyzed on a voxel-by-voxel basis, the 5-HT2AR binding potential being determined for each voxel using the pseudoequilibrium ratio method on PET data obtained 65–90 min after the radiotracer bolus injection. Again, no significant between-group differences were found. Furthermore, no significant correlations were observed between any of 5 factors (negative, positive, activation, dysphoric, and autistic preoccupation) derived from the positive and negative syndrome scale for typologic and dimensional assessment (83) and 5-HT2AR binding potential (82). However, using 18F-setoperone PET to study 6 antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia patients and 7 healthy controls, Ngan et al. (84) have reported results consistent with postmortem findings. A nondirected voxel-based analysis of the entire search volume showed that 5-HT2AR binding potential in the frontal cortex was significantly smaller in schizophrenia; this smaller binding potential is likely to have been present at illness onset, before antipsychotic exposure (84).
5-HT2A PET studies have yielded valuable data on antipsychotic drug binding to cortical 5-HT2AR. Trichard et al. (85) used 18F-setoperone PET to compare the binding of therapeutic doses of chlorpromazine, clozapine, and amisulpride. A dose-dependent decrease in the number of available cortical binding sites for 18F-setoperone was found in the chlorpromazine group; for the highest dose, there was a virtual lack of sites available for binding. A low percentage of available binding sites was also found in the clozapine-treated patients at all doses; no significant binding of amisulpride was detected. These findings suggest a high level of 5-HT2A blockade with both the archetypal atypical antipsychotic clozapine and the high doses of the archetypal typical antipsychotic chlorpromazine (85). Although amisulpride has no 5-HT2A blockage efficacy, it is still an effective antipsychotic medication. To study the binding characteristics of the atypical antipsychotic quetiapine, patients were treated with different quetiapine doses and 11C-raclopride and 11C-N-methylspiperone PET used to study cortical D2 and 5HT2A occupancies, respectively (86); a pattern of high 5HT2AR and lower D2R blockade occurred. Similarly, an 11C-raclopride and 18F-setoperone PET study of the atypical antipsychotic ziprasidone in schizophrenia or schizoaffective patients showed greater 5HT2AR than D2R occupancy at therapeutic doses (87). PET has been used to examine other serotonin receptors (such as 5HT1A) (88) and transporters (89).
PET IN IDENTIFICATION OF REGIONAL BRAIN ABNORMALITIES IN SCHIZOPHRENIA
Use of Imaging
A variety of PET tracers has been used to identify brain abnormalities.
11C Studies.
The PFC and striatum play an important role in schizophrenia (51). They highly express D1 and D2 receptors, respectively. Other regions that play a part do not contain D2Rs but do contain a substantial number of D1Rs in specific regions such as the cingulate gyrus, temporal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus (90). Okubo et al. (51) used 11C PET to map D1/D2 receptors in the human brain. They found no differences in the striatum in schizophrenia patients, compared with control subjects, but reduced prefrontal cortical D1R signaling was observed in those with schizophrenia. Lindström et al. (7) reported heightened dopamine synthesis in the medial PFC and striatum in patients with schizophrenia, compared with controls (Fig. 3). A recent metaanalysis showed a small but significantly heightened level of striatal D2Rs in unmedicated patients (91).
Patlak slope images of schizophrenia patients (n = 12) (left) and healthy volunteers (n = 10) (right). Images were averaged over all subjects in each group after matching images to standard stereotactic brain atlas. The following anatomic structures are outlined by color code: yellow = outline of brain, caudate nucleus, and putamen; white = Brodmann area 10 (prefrontal cortex); black = Brodmann areas 21, 22, and 37 (temporal cortex); and red = Brodmann area 24 (caudal medial prefrontal cortex). (Reprinted with permission of (7).)
18F-Fallypride Studies.
18F-fallypride or 11C-fallypride is a dopamine receptor ligand with high affinity and specificity (92). PET 11C studies show a decline in D1R binding potential of 7%−9% per decade in the putamen, caudate nucleus, frontal cortex, and occipital cortex (93).
Buchsbaum et al. (94) coregistered 18F-fallypride PET and MRI in drug-naïve schizophrenia and matched controls. Schizophrenia was associated with reduced extrastriatal D2R/D3R availability in the thalamus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, and temporal cortex, with the largest reduction occurring in the thalamus, which contains 10 times fewer D2Rs than does the striatum (95). PFC neurons express 4–7 times more D1Rs than D2Rs in schizophrenia (93). The latter group showed that there is a high correlation between task and thalamic dopamine released, indicating extrastriatal dopamine involvement in normal cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders.
l-3,4-Dihydroxy-6-18F-Fluorophenylalanine (18F-FDOPA) Studies.
Since its introduction by Garnett et al. (96,97), 18F-FDOPA has been used to study presynaptic dopamine metabolism in neuropsychiatric disorders. It is taken up by presynaptic monoaminergic neurons and decarboxylated to 18F-flourodopamine, which is taken up and stored in nerve terminal vesicles. Reith et al. (5) showed increased 18F-FDOPA decarboxylase activity in the neostriatum in schizophrenia. Firnau et al. (98) showed increased 18F-FDOPA uptake in the PFC and anterior cingulate in humans. Hietala et al. (6) demonstrated increased 18F-FDOPA uptake in the putamen and caudate in drug-naïve schizophrenia patients.
Neuroleptics can highlight changes in the expression of dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia and dopaminergic systems. Medication-free schizophrenia patients show reduced 18F-FDOPA uptake in the ventral striatum and increased uptake in the posterior cingulate (99).
Graphical Analysis
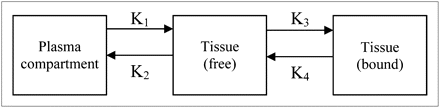
Compartmental analysis can be used when determining tracer binding kinetics (100). It models tracer uptake by separating the effects of transport from those of receptor binding by creating linear plots and solving differential equations that represent the latter. The plot slope approximately equates to the distribution volume and plasma contribution and is related to the number of tracer binding sites. Model parameters are determined by fitting the models to the PET data collected using several assumptions and approaches. Graphical models can be created for both reversible and irreversible tracers. The models used to describe uptake and binding of PET tracers can consist of 2 or more compartments, with transfer constants describing the uptake and reversibility of the tracer (Fig. 4). The models for reversible and irreversible tracers differ in that the final compartment of the model for irreversible tracers has transfer constants such that the binding of the tracer to the receptor or bound tissue (k3) is nonzero and the dissociation from the specific binding (k4) is zero, because irreversible tracers are trapped during scanning.
Three-compartment model for reversible or irreversible tracers. For irreversible tracers, transfer constant K4 = 0.Transfer constants K1, k2, k3, and k4 describe uptake between plasma and free tissue, free tissue to plasma, binding of tracer to receptor or bound tissue, and dissociation from specific binding, respectively.
18F-Fallypride Studies.
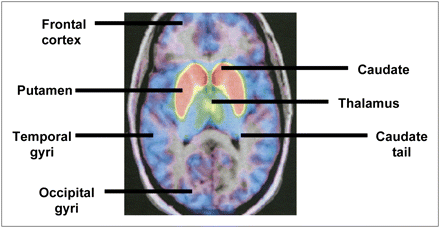
Dopamine receptors in schizophrenia have been investigated using 18F-fallypride. Mukherjee et al. (101) studied D2R and D3R distribution in healthy unmedicated, caffeine-free (for at least 4 h) volunteers using 18F-fallypride PET and coregistered MR images. Images were corrected for subject motion by realignment of the dynamic PET datasets to a reference summed image (102). The PET data were then analyzed using graphical methods, with the cerebellum as a reference region because it has minimal specific binding to dopaminergic sites. Time–activity curves and a pixel-by-pixel parametric image of the distribution volume ratio using an ROI-based approach were created (103). The highest concentration was found in the putamen, followed by (in descending order) the caudate, thalamus, amygdala, substriatal region, hippocampus equal to temporal cortex, and orbitofrontal cortex (lowest concentration). There was a greater than 10% decrease in 18F-fallypride binding per decade, which is in line with previous studies (104,105) and may result from progressive-free radical change, loss of proteins because of inefficient recycling, and cell death (Fig. 5) (106).
18F-fallypride PET–MR coregistered images showing head of caudate, putamen, and tail of caudate. (Reprinted with permission of (101).)
15O-Water Studies.
Andreasen et al. (107) studied a group of patients with schizophrenia undergoing 15O-H2O PET to examine putative cognitive deficits. The fraction of radioisotope in arterial plasma was fitted to a biexponential function and used to correct the plasma-measured input function for blood-borne metabolites. Two tasks were performed to determine whether brain abnormalities were intrinsic or secondary to task performance. In the first task (practical recall), the neural simulation would be equivalent to that of healthy volunteers, and in the second (novel recall) these would differ. PET showed the presence of a prefrontal–thalamic–cerebellar network that is activated in controls but dysfunctional in schizophrenia, suggesting cognitive dysmetria (the inability to receive and process information rapidly and effectively); patients have complex circuits that may display varying patterns of disruption depending on the task.
18F-FDOPA Studies.
18F-FDOPA has been used to investigate presynaptic striatal dopaminergic function in neurologic disorders. Compartmental modeling helps to distinguish controls from patients with neurologic disorder. Kawatsu et al. (108) compared different analysis methods for irreversible and reversible tracer kinetic models. Logan analysis (103,109) more accurately represents tracer modeling in tissues with no irreversible components (e.g., the reference tissues), compared with Patlak analysis (110,111), which assumes there is an irreversible compartment. Also, Logan analysis is theoretically more stable during short scan times in dynamic studies, providing accurate quantification for dynamic 18F-FDOPA data.
Patlak analysis was used with ROI analysis by McGowan et al. (68) to show increased presynaptic striatal 18F-FDOPA uptake and decreased prefrontal cortical uptake in medicated schizophrenia patients. Studies on medicated patients elucidate the effects of medication on decarboxylase activity, which influences the rate of dopamine synthesis (112). This regional dopamine dysfunction has previously been shown in unmedicated schizophrenia patients (49,51).
More recently, Howes et al. (113) used 18F-FDOPA to investigate a putative association between striatal dopaminergic function, symptomatology, and neuropsychologic functioning using Patlak analysis. Patients with prodromal schizophrenia symptoms showed heightened striatal 18F-FDOPA uptake, which gradually reached the level in those with schizophrenia. Increased striatal dopamine uptake positively correlated with severity of prodromal symptom and performance on neuropsychologic tasks.
PET IN IDENTIFICATION OF BRAIN REGIONS ASSOCIATED WITH COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING
Cognition is considered an extension of the clinical phenotype of the schizophrenia syndrome (23,114). Studying the relationship between specific brain abnormalities and cognitive functioning in schizophrenia can enable us to identify abnormal regions and neurocircuitry. Frith (115) modeled cognitive processes in schizophrenia using PET studies showing regional cerebral blood flow differences.
Brain metabolism and function are used to assess functional changes associated with the dopaminergic system. Cerebral blood blow is often used to index brain function. Increased motor function is associated with increased regional cerebral blood flow, mapped using a PET tracer specifically water-labeled with 15O. PET allows detailed mapping of motor function or cognitive processes such as language, attention, memory, and emotion. Regions activated during specific tasks have increased radionuclide uptake. These images are quantified by drawing ROIs around activated regions and comparing psychiatric disorders and controls. Using 15O-water PET, Crespo-Facorro et al. (116) investigated cognitive dysmetria in medication-free schizophrenia patients and controls by examining verbal learning and recognition. During recall of well-learned word lists, schizophrenia patients did not show activation in cortical–cerebellar–thalamic–cortical circuitry.
Neuroleptics may lead to emotional changes in schizophrenia patients. Paradiso et al. (117) performed 15O-water PET studies on patients who were antipsychotic-free for at least 3 wk. They were exposed to pleasant and unpleasant stimuli. They showed no activation in the PFC and decreased thalamic and cerebral blood flow, suggesting dysfunctional connectivity.
Hypofrontality is an abnormality in brain function in which there is reduced activation in the frontal (especially prefrontal) cortex. Weinberger et al. (118,119) showed that patients were hypofrontal (independent of medication effects) during performance on the Wisconsin card sorting test (WCST), a measure of executive function and problem-solving ability that assesses prefrontal cortical functioning. Numerous resting-state studies in schizophrenia have shown hypofrontality, particularly in chronic schizophrenia (120), and in psychomotor syndrome (121,122). Frontal activation is associated with cognitive performance. Fletcher et al. (123) used the California verbal learning test to show reduced frontal activation, and therefore impaired performance, during a high-processing load subtest. Similarly, some studies (124,125) have reported that reduced frontal activation in schizophrenia during a working memory task (n-back task) occurs only when there is high memory load and impaired performance. These studies indicate the importance of task difficulty on frontal lobe activation in schizophrenia.
The dorsolateral PFC plays a role in resolving conflict between competing responses (126). Reduced dopaminergic activity may contribute to impaired activity or function in schizophrenia. For instance, Weinberger et al. (119) showed a correlation between impaired prefrontal activation during the WCST and low cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid (a dopamine metabolite). Amphetamines (indirect dopaminergic agonists) can, at least to some extent, help reverse poor frontal activation to WCST (127). Specific genes for schizophrenia also play a role, whereby those with slower dopamine catabolism (because of COMT variation) have a more efficient prefrontal response (39). Recently, however, hypofrontality has been considered an inconsistent finding that varies with task and symptomatology (128). Hypofrontality is present at rest and results in reduced activation of the frontal regions (129,130).
Several studies have investigated the association between the PFC and performance on executive functioning and attention tasks. Andreasen et al. (122) showed decreased prefrontal activation using SPECT in patients with predominantly negative symptoms with the Tower of London paradigm. Heckers et al. (131) identified changes in episodic memory in schizophrenia, suggesting that during these tasks patients have normal dorsolateral PFC functioning but reduced hippocampal activation. Christian et al. (132) reported a positive correlation between performance on a spatial attention task and dopamine release in the thalamus.
DISCUSSION
The dopamine hypothesis explains how an individual with neurodevelopmental deviance, or an isolated adolescent with bizarre ideas, transforms into an actively psychotic individual. Converging lines of evidence suggest dopamine dysregulation in schizophrenia (3,60,133).
PET tracers used to identify brain abnormalities include 11C PET, 15O-water, 18F-fallypride, and 18F-FDOPA. Some tracers used in PET neuroimaging require radioactive isotopes of short half-lives, therefore requiring a cyclotron close by. Also, the radiation dose may restrict repeated scanning. Some studies used compartmental modeling to determine tracer binding kinetics. These studies show increased dopamine content and higher D2R density in schizophrenia.
PET has identified regions associated with cognitive functioning in schizophrenia. Earlier human PET studies focused on the relationship between dopamine neurotransmission and cognitive functioning while patients were in states of acute or florid illness. One such study showed a positive correlation between working memory and blood–brain 18F-FDOPA clearance in schizophrenia (69); heightened striatal 18F-FDOPA use in patients also occurred (5,6).
PET allows the assessment of brain receptor binding and mapping of regional cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism during cognitive activation. 15O-water studies (116) showed a significant variation between patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls—variation that was not a consequence of the reduction in blood flow seen in schizophrenia but probably caused by a disruption in neural connectivity (i.e., dopamine dysregulation).
Some studies have investigated the effect of medication on tracer-receptor binding. Amphetaminelike drugs cause an increase in striatal dopamine in schizophrenia (70). Antipsychotic medication increases D2R densities in schizophrenia (72).
CONCLUSION
PET imaging provides substantial insights into the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Although this imaging technique involves exposure to ionizing radiation and is expensive, compared with MRI, it is particularly valuable in understanding the neurobiological mechanisms underpinning schizophrenia. Future neuroimaging work should further elucidate the association between brain abnormalities, genetic underpinnings, and cognitive functioning in schizophrenia.
Footnotes
-
COPYRIGHT © 2010 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine, Inc.
References
- 1.↵
- 2.↵
- 3.↵
- 4.↵
- 5.↵
- 6.↵
- 7.↵
- 8.↵
- 9.↵
- 10.↵
- 11.↵
- 12.↵
- 13.↵
- 14.↵
- 15.↵
- 16.↵
- 17.↵
- 18.↵
- 19.↵
- 20.↵
- 21.↵
- 22.↵
- 23.↵
- 24.↵
- 25.↵
- 26.↵
- 27.↵
- 28.↵
- 29.↵
- 30.↵
- 31.↵
- 32.↵
- 33.↵
- 34.↵
- 35.↵
- 36.↵
- 37.↵
- 38.↵
- 39.↵
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.↵
- 44.↵
- 45.↵
- 46.↵
- 47.↵
- 48.↵
- 49.↵
- 50.↵
- 51.↵
- 52.↵
- 53.↵
- 54.↵
- 55.↵
- 56.↵
- 57.↵
- 58.↵
- 59.↵
- 60.↵
- 61.↵
- 62.↵
- 63.↵
- 64.↵
- 65.↵
- 66.↵
- 67.↵
- 68.↵
- 69.↵
- 70.↵
- 71.↵
- 72.↵
- 73.↵
- 74.↵
- 75.↵
- 76.↵
- 77.↵
- 78.↵
- 79.↵
- 80.↵
- 81.↵
- 82.↵
- 83.↵
- 84.↵
- 85.↵
- 86.↵
- 87.↵
- 88.↵
- 89.↵
- 90.↵
- 91.↵
- 92.↵
- 93.↵
- 94.↵
- 95.↵
- 96.↵
- 97.↵
- 98.↵
- 99.↵
- 100.↵
- 101.↵
- 102.↵
- 103.↵
- 104.↵
- 105.↵
- 106.↵
- 107.↵
- 108.↵
- 109.↵
- 110.↵
- 111.↵
- 112.↵
- 113.↵
- 114.↵
- 115.↵
- 116.↵
- 117.↵
- 118.↵
- 119.↵
- 120.↵
- 121.↵
- 122.↵
- 123.↵
- 124.↵
- 125.↵
- 126.↵
- 127.↵
- 128.↵
- 129.↵
- 130.↵
- 131.↵
- 132.↵
- 133.↵
- Received for publication June 24, 2009.
- Accepted for publication December 21, 2009.