Abstract
Several bone-seeking radionuclides (32P, 89Sr, 186Re, and 153Sm) have been used to treat bone pain. The limiting factor in this modality is marrow toxicity. Our hypothesis is that marrow toxicity can be reduced while maintaining therapeutic efficacy using radionuclides that emit short-range β particles or conversion electrons (CEs). A recent study on 47 patients using the short-range CE emitter 117mSn(4+)diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (117mSn(4+)DTPA) supports this hypothesis. The hypothesis is now tested using 117mSn(4+)DTPA in a mouse femur model. Methods: The survival of granulocyte–macrophage colony-forming cells (GM-CFCs) in femoral marrow is used as a biologic dosimeter for bone marrow. The dosimeter is calibrated by irradiating mice with exponentially decreasing dose rates of 137Cs γ-rays with a dose-rate decrease half-time, Td, equal to the effective clearance half-time of 117mSn(4+)DTPA from the femur (222 h). When Td = 222 h, the mean absorbed dose required to achieve a survival fraction of 37% is 151 cGy. After calibration, 117mSn(4+)DTPA is administered and GM-CFC survival is determined as a function of injected activity. These data are used to experimentally determine the mean absorbed dose to the femoral marrow per unit injected activity. The kinetics of radioactivity in the marrow, muscle, and femoral bone are also determined. Finally, a theoretic dosimetry model of the mouse femur is used, and the absorbed doses to the femoral marrow and bone are calculated. Results: The experimental mean absorbed dose to the femoral marrow per unit injected activity of 117mSn(4+)DTPA is 0.043 cGy/kBq. The theoretic mean absorbed dose to the femoral bone per unit injected activity is 1.07 cGy/kBq. If these data are compared with those obtained previously for 32P-orthophosphate, the radiochemical 117mSn(4+)DTPA yields up to an 8-fold therapeutic advantage over the energetic β emitter 32P. Conclusion: The CE emitter 117mSn offers a large dosimetric advantage over energetic β-particle emitters for alleviating bone pain, and possibly for other therapeutic applications, while minimizing marrow toxicity.
- bone
- pain
- metastases
- radionuclides
- granulocyte–macrophage colony-forming cells
- chronic irradiation
- dose–response
- dosimetry
- EGS4
- 32P
- 33P
- 117mSn
- therapy
Several bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals have been used to treat bone pain caused by osteometastases (1–4). About 65%–85% of patients experience substantial pain relief by these therapeutic agents (1,5). Radioactive phosphorus (32P) was the first radionuclide to be used in bone pain palliation therapy (6); however, other radiochemicals, including 89Sr-chloride (2,7,8), 85Sr-chloride (9), 186Re-1,1-hydroxyethylidene diphosphonate (10–12), and 153Sm-ethylenediaminetetramethylenephosphonic acid (13–15), have been used subsequently for this purpose.
The major dose-limiting factor in this modality is bone marrow toxicity, which leads to a decrease in peripheral blood cell counts (1,16). The bone marrow absorbed dose is imparted by radiation emitted by radioactive decays in four principal source compartments: marrow, endosteum, bone matrix, and all other surrounding organs. The radiochemicals that have been used (or proposed for use) in bone palliation therapy localize predominantly in the skeletal tissues and emit a high yield of β particles (Table 1). Therefore, the marrow absorbed dose can be primarily attributed to decays in the first three compartments. Given that these radiopharmaceuticals selectively localize in bone and concentrate in the bony lesions, it has been suggested that use of low-energy electron emitters (e.g., short range) might reduce the bone marrow toxicity while selectively increasing the dose to the bone matrix (17–20). In an earlier study in mice using the colony-forming units per spleen assay, therapeutic doses of 117mSn were shown to offer an almost 30-fold bone marrow–sparing advantage over 32P (21). Using a murine model, Goddu et al. (20) showed that the low-energy β emitter 33P offers a 3- to 6-fold therapeutic advantage over the energetic β emitter 32P. Atkins et al. (22) and Srivastava et al. (23) used the low-energy conversion electron (CE) emitter 117mSn (117mSn(4+)diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid [DTPA]) to treat bone pain in patients and found effective pain relief with no significant myelotoxicity.
Radionuclide Properties
Although pharmacokinetic data have been obtained for 117mSn(4+)DTPA (23–25), to our knowledge, no detailed study has been performed to study the bone and bone marrow dosimetry characteristics of this radionuclide. This work quantitates the capacity of 117mSn(4+)DTPA to irradiate bone tissue while minimizing the absorbed dose to bone marrow. A combination of experimental and theoretic approaches based on a mouse model is used to make this comparison. Femoral bone marrow granulocyte–macrophage colony-forming cell (GM-CFC) survival is used to experimentally ascertain bone marrow toxicity and absorbed dose from this radiopharmaceutical after its intravenous administration (26,27). A theoretic approach is used to calculate the absorbed dose delivered to the bone matrix. The results are used to dosimetrically compare 117mSn(4+)DTPA with the low- and high-energy β-particle–emitting radiopharmaceuticals, 33P-orthophosphate and 32P-orthophosphate, respectively, for palliation of bone pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Biologic Dosimetry Using GM-CFC Survival
GM-CFC survival was used as a biologic dosimeter to determine the bone marrow absorbed dose in mice. GM-CFCs are progenitor cells that reside in the marrow compartment. Therefore, the absorbed dose received by the bone marrow can be determined by monitoring the survival of these cells provided that the system is properly calibrated. Details on the use of GM-CFC as a biologic dosimeter have been described (20,27). Female Swiss Webster mice (age, 5–6 wk; weight, 25 ± 2 g) were obtained from Taconic Farms (Germantown, NY). The animals were acclimated in the university research animal facility (University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey) for 1 wk before use. Food and water were provided ad libitum.
Radionuclide and its Administration
The radiochemical 117mSn(4+)DTPA was kindly provided by Diatide, Inc. (Londonderry, NH), as an aqueous solution of stannic DTPA (294.7 MBq/mL) in 1 mL water. The radiochemical was diluted with phosphate-buffered saline to the desired concentration. Mice, in groups of four, were injected intravenously with 0.2 mL solution containing the radiochemical through the lateral tail vein.
Radionuclide Kinetics and Optimal Day for GM-CFC Survival Assay
The biokinetics of 117mSn(4+)DTPA was obtained as follows. Animals, in groups of four, were injected intravenously with an equal activity of radiochemical (240 kBq/0.2 mL). Animals were killed on 0.21, 0.67, 1.25, 2.29, 5, 7, 14, 21, and 30 d after injection and the femurs were resected. The muscle surrounding the femur was removed and the muscle and femur were transferred to separate preweighed 12 × 75 mm glass tubes. The activities in the muscle and femur were determined using a NaI scintillation well counter with window levels set on the 156.0- and 158.6-keV photopeaks (combined yield, 0.885; efficiency, 0.62) of 117mSn. The marrow was flushed from the femurs, and the activity in aliquots of the marrow suspension along with the activity remaining in the femur were determined. Femur and muscle weights were determined in each case. The activities in muscle, bone matrix, and marrow compartments were thus determined as a function of time after injection.
The optimal day to assay GM-CFC survival (day after injection on which nadir occurs) was determined as follows. Animals, in groups of four, were injected intravenously with an equal amount of radiochemical on 5, 7, and 9 d before the date of killing. In addition, two untouched groups were maintained as control animals. Experiments were performed for two different injection activities (370 and 5846 kBq/0.2 mL) to ensure that injected activity did not influence the optimal day. All groups were killed on the same day and assayed for GM-CFC survival; the survival fraction compared with control animals was plotted as a function of time after injection.
GM-CFC Survival Assay
The experimental protocols adopted from Metcalf (28) and described in our earlier article (27) were used for determination of GM-CFC survival. Preparation of the different culture media required for the assay has been described (27). Briefly, the animals were killed by cervical dislocation and immersed in 70% ethanol, and the femurs were separated under aseptic conditions (laminar flow hood) using sterile instruments. Marrow from these femurs was flushed with 1 mL wash medium into a 50-mL tube using a 3-mL syringe fitted with a 21-gauge needle. After aspirating the medium through the femur shaft several times, an additional 3 mL fresh medium were flushed through the femur. The cell suspension was centrifuged, the supernatant was decanted, and the pellet was resuspended in 5 mL wash medium. The mononucleated cell fraction was separated from the crude bone marrow suspension by gently layering 5-mL cell suspension on top of 3.5 mL Histopaque-1077 (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO) and centrifuging at 400g for 30 min at 4°C. The mononucleated cell layer was removed carefully with a 3-mL syringe, washed three times with 15 mL wash medium, and resuspended in 2 mL double-strength culture medium. The number of mononucleated cells corresponding to each group was counted using a model ZM cell counter (Coulter Electronics, Hiahleah, FL). Three dilutions of the resulting mononucleated cells were plated for colony formation by mixing with equal volumes of double-strength culture medium and 0.6% Bacto agar solution (DIFCO, Detroit, MI) in the presence of 1200 U (20 μL) of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (Sigma). The plates remained at room temperature until the agar gelled firmly (10–15 min), whereupon they were transferred to an incubator at 37°C with 100% humidity, 5% CO2:95% air, for 7 d to allow colony formation. The resulting GM-CFC colonies were scored with an Olympus dissection microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at 40× magnification, and the survival fraction compared with that of the unirradiated control animals was determined.
GM-CFC Survival Versus Femoral Activity
GM-CFC survival was determined as a function of injected activity for 117mSn(4+)DTPA. Six groups (four mice per group) of mice were injected with a fixed 0.2-mL volume containing different activities of the radiochemical. The animals were killed on the optimal day (seventh day after injection; Results) and assayed for GM-CFC survival. The femoral bones, having been purged of marrow for the survival assay, were dried, weighed, and assayed for activity content as described. Activities in the flushed bone marrow samples were also determined. The extrapolated initial activities were obtained by correcting these activities to the time of injection using the physical half-life of the radionuclides and the effective half-times of the radiochemical in the femurs obtained in the biokinetics experiments.
Calibration of Biologic Dosimeter
The biologic dosimeter, survival of GM-CFC (27), was calibrated using our custom-designed low-dose-rate 137Cs irradiator (equipped with computer-controlled mercury attenuator system), which facilitates the delivery of exponentially decreasing dose rates (26). This irradiator allows simultaneous irradiation of mice (groups of four) with different initial dose rates by placing different groups of mice at different distances from the 137Cs source. Although the initial dose rates were different for each group of mice, the dose rates to each group were exponentially decreased using a dose-rate decrease half-time of 9.2 d, which is equal to the effective half-time of the radiochemical in the femoral bone (Results). Animals were taken out of the irradiator on the optimal day (see above), killed, and assayed for GM-CFC cell survival.
Theoretic Mean Absorbed Dose to Femoral Bone and Bone Marrow
The theoretic absorbed doses received by femoral bone and bone marrow from 117mSn(4+)DTPA are calculated using a theoretic dosimetry model of the mouse femur that is described in detail elsewhere (20). Briefly, the model consists of four source regions (marrow, endosteum, bone matrix, and muscle) and three target regions (endosteum, bone matrix, and bone marrow). The EGS4 Monte Carlo radiation transport code is used to calculate absorbed fractions, which in turn are used to calculate the mean absorbed dose to the target regions in the mouse femur per unit cumulated activity in a given source region of the femur S(target ← source) (20). The theoretic S values for 117mSn are given in Table 2. The total theoretic absorbed dose to the target per unit administered activity is given by (29):
 Eq. 1
Eq. 1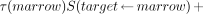
 where AInj is the injected activity, and τ(source) is the residence time in the source region. This is defined as τ(source) = Ã(source)/AInj, where Ã(source) is the cumulated activity in the source region. These quantities are given in Table 3 for 117mSn(4+)DTPA for each source region.
where AInj is the injected activity, and τ(source) is the residence time in the source region. This is defined as τ(source) = Ã(source)/AInj, where Ã(source) is the cumulated activity in the source region. These quantities are given in Table 3 for 117mSn(4+)DTPA for each source region.
Theoretic S Values for 117mSn (cGy/kBq/h)*
Theoretic Absorbed Dose to Marrow from 117mSn(4+)DTPA
RESULTS
Radionuclide Kinetics
Figure 1 shows the effective uptake and clearance of 117mSn(4+)DTPA in mouse femoral bone, femoral marrow, and muscle surrounding the femur after intravenous administration of this radiochemical. The kinetics data were least-squares fit to the two-component exponential function given by Equation 2.
 Eq. 2The fitted values for muscle are k = 0.65, a = 0.94, Te1 = 0.50 d, and Te2 = 5.0 d. A single-component fit emerges for bone and marrow. For femoral marrow, a = 1, k = 0.81, and Te1 = 10.5 d. Finally, for femoral bone, a = 1, k = 42.3, and Te1 = 9.2 d.
Eq. 2The fitted values for muscle are k = 0.65, a = 0.94, Te1 = 0.50 d, and Te2 = 5.0 d. A single-component fit emerges for bone and marrow. For femoral marrow, a = 1, k = 0.81, and Te1 = 10.5 d. Finally, for femoral bone, a = 1, k = 42.3, and Te1 = 9.2 d.
Effective clearance of radioactivity from murine femoral bone (△), bone marrow (○), and muscle (□) after intravenous administration of 117mSn(4+)DTPA. Data are presented as percentage injected activity per gram (%IA/g) of tissue. Data from two independent experiments are plotted.
The extrapolated initial activity, Ao, in the femoral bone is plotted as a function of the injected activity, AInj,in Figure 2. The extrapolated initial activity was linearly dependent on the injected activity according to the relationship,
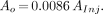 Eq. 3These results indicate that 0.86% of the injected 117mSn quickly localizes in each femoral bone.
Eq. 3These results indicate that 0.86% of the injected 117mSn quickly localizes in each femoral bone.
Extrapolated initial uptake of radioactivity in femoral bone as function of injected activity after intravenous administration of 117mSn(4+)DTPA. Uptake is linearly proportional to injected activity. Data for several independent experiments are denoted by different symbols.
Optimal Day
The optimal day to assay GM-CFC survival is the day on which the survival is minimum (nadir). The survival of GM-CFCs as a function of time after injection of 117mSn(4+)DTPA is shown in Figure 3. As in our previous studies with 90Y-citrate, 32P-orthophosphate, and 33P-orthophosphate, the survival fraction reaches a minimum on the seventh day after injection and it is independent of the injected activity over the range studied (20,27).
GM-CFC Survival Versus Activity
Figure 4 shows the GM-CFC survival fraction as a function of both the injected activity and the extrapolated initial femoral bone activity. The data were least-squares fit to a simple exponential function given by Equation 4.
 Eq. 4where SF is the fraction of GM-CFC survival, Ao is the extrapolated initial femoral bone activity, Ao,37 is the extrapolated initial femoral bone activity required to achieve 37% GM-CFC survival, AInj is the activity injected into each mouse, and AInj,37 is the injected activity required to achieve 37% GM-CFC survival. The fitted value for Ao,37 was 30.2 ± 0.8 kBq per femoral bone and the AInj,37 was 3546 ± 88 kBq.
Eq. 4where SF is the fraction of GM-CFC survival, Ao is the extrapolated initial femoral bone activity, Ao,37 is the extrapolated initial femoral bone activity required to achieve 37% GM-CFC survival, AInj is the activity injected into each mouse, and AInj,37 is the injected activity required to achieve 37% GM-CFC survival. The fitted value for Ao,37 was 30.2 ± 0.8 kBq per femoral bone and the AInj,37 was 3546 ± 88 kBq.
Survival of GM-CFCs as function of extrapolated initial activity in femoral bone (lower abscissa) and injected activity (upper abscissa) after intravenous administration of 117mSn(4+)DTPA. Animals were killed on seventh day after injection, the optimal day for GM-CFC assay (Fig. 3). Data from several different experiments are indicated by different symbols.
Calibration of Biologic Dosimeter
The survival of GM-CFCs as a function of initial dose rate (cGy/h) delivered by the 137Cs irradiator is shown in Figure 5 for a dose-rate decrease half-time, Td = 9.2 d. The data were least-squares fit to Equation 5:
 Eq. 5where ro is the initial dose rate (cGy/h) and ro,37 is the initial dose rate required to achieve 37% GM-CFC survival. The fitted value of ro,37 was 1.17 ± 0.05 cGy/h.
Eq. 5where ro is the initial dose rate (cGy/h) and ro,37 is the initial dose rate required to achieve 37% GM-CFC survival. The fitted value of ro,37 was 1.17 ± 0.05 cGy/h.
Survival of GM-CFCs as function of initial dose rate (lower abscissa) and absorbed dose (upper abscissa). Mice were irradiated chronically with exponentially decreasing dose rates (dose-rate decrease half-time = 222 h) of external 137Cs γ-rays (26) and killed on seventh day after initiation of irradiation. Absorbed dose is calculated by integrating dose rate over 7-d irradiation period. Open and closed symbols represent data for two independent experiments.
The cumulated absorbed dose, D, delivered by the irradiator over the 7-d irradiation period is given by:
 Eq. 6The initial dose rate ro was different for each group of animals. The ordinate and upper abscissa of Figure 5 show the GM-CFC survival as a function of absorbed dose received by the marrow. A least-squares fit of the data to the function,
Eq. 6The initial dose rate ro was different for each group of animals. The ordinate and upper abscissa of Figure 5 show the GM-CFC survival as a function of absorbed dose received by the marrow. A least-squares fit of the data to the function,
 Eq. 7yields the dose required to achieve 37% survival, D37. For the dose-rate decrease half-time of 222 h, D37 = 151 ± 7 cGy. As indicated above, this half-time corresponds to the effective clearance half-time of 117mSn(4+)DTPA from the femoral bone. This D37 can be compared with our previously obtained values of 144 ± 15, 132 ± 12, 129 ± 3, and 133 ± 10 cGy for dose-rate decrease half-times of 62, 255, and 425 h and ∞ (constant dose rate), respectively (20,27).
Eq. 7yields the dose required to achieve 37% survival, D37. For the dose-rate decrease half-time of 222 h, D37 = 151 ± 7 cGy. As indicated above, this half-time corresponds to the effective clearance half-time of 117mSn(4+)DTPA from the femoral bone. This D37 can be compared with our previously obtained values of 144 ± 15, 132 ± 12, 129 ± 3, and 133 ± 10 cGy for dose-rate decrease half-times of 62, 255, and 425 h and ∞ (constant dose rate), respectively (20,27).
This new datum supports our earlier conclusion that differences in dose rate (0.25–8 cGy/h) among these various dose-rate decrease half-times do not play a major role in determining the survival of GM-CFCs over the range of initial dose rates, total doses, and irradiation times considered in these experiments (20). Rather, the total dose delivered is of primary importance. This conclusion is based on integration of the absorbed dose rate over 7 d (Eq. 6). Very disparate D37 values would emerge if the integration was performed to infinity (e.g., integration of constant dose rate to infinite time yields infinite absorbed dose), thereby emphasizing the importance of integrating over a time that is relevant to the biologic endpoint that is studied (30,31).
Experimental and Theoretic Mean Absorbed Doses
The mean absorbed dose to murine femoral marrow from 117mSn is principally from decays that occur in two compartments: femoral marrow and femoral bone matrix. The response of the biologic dosimeter (GM-CFC survival) registers the total dose from decays that occur in these source regions. By equating Equations 4 and 7, the experimental mean absorbed dose to bone marrow per unit injected activity D(marrow)/AInj is given by:
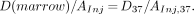 Eq. 8The experimental D(marrow)/AInj for 117mSn(4+)DTPA is 0.043 ± 0.002 cGy/kBq.
Eq. 8The experimental D(marrow)/AInj for 117mSn(4+)DTPA is 0.043 ± 0.002 cGy/kBq.
The theoretic absorbed dose to femoral marrow per unit injected activity, assuming a uniform distribution of 117mSn in the femoral bone matrix, is calculated according to Equation 1 to be D(marrow)/AInj = 0.071 cGy/kBq. This quantity is given in Table 3 along with a breakdown of the contributions from the various source compartments. The theoretic mean absorbed dose to the bone matrix D(matrix)/AInj = 1.07 cGy/kBq (Table 4).
Theoretic Absorbed Dose to Bone from 117mSn(4+)DTPA
DISCUSSION
The effective clearance half-time from the femoral bone is 9.2 d for 117mSn(4+)DTPA. Given that 117mSn has a physical half-life of 13.9 d, this corresponds to a biologic clearance half-time of 27.2 d. This biologic half-time is somewhat longer than the half-time of 16.5 d observed by Swailem et al. (25) in BALB/c mice. Our data for bone may be compared with the data obtained for humans where no clearance from bone was observed (25). Interestingly, the effective clearance half-time from marrow (10.5 d) is slightly longer than from bone. It is possible that this long half-time may be due to radioactivity bound to small bone spicules that may be dislodged from the marrow cavity during the flushing procedure. Muscle surrounding the femur showed rapid uptake of the radiopharmaceutical followed by two-component exponential clearance (Fig. 1). Ninety-four percent of the muscle radioactivity cleared quickly with a 0.5-d effective half-time, and the remaining 6% cleared with an effective half-time of 5 d. The residence time for the 117mSn(4+)DTPA in the muscle surrounding the femur was only 0.0693 h compared with 3.7 and 5.3 h for 32P- and 33P-orthophosphate, respectively (Table 5). Finally, like 90Y-citrate and 32P- and 33P-orthophosphate (20,27), the uptake of 117mSn(4+)DTPA in femoral bone showed a linear dependence on injected activity (0.86% AInj per femoral bone) over the range studied (Fig. 2 and Eq. 3). The magnitude of the uptake was similar to the values of 0.80% and 0.67% observed for 90Y-citrate (27) and the orthophosphate radiochemicals (20), respectively.
Comparison of Radiopharmaceuticals
The experimental mean absorbed dose to bone marrow per unit injected activity, D(marrow)/AInj, for 117mSn(4+)DTPA is 0.043 ± 0.002 cGy/kBq. This is very similar to the value of 0.047 ± 0.010 cGy/kBq that was obtained earlier for 33P-orthophosphate, an emitter of low-energy β particles (20). However, the theoretic absorbed dose estimate yields a value of D(marrow)/AInj = 0.071 cGy/kBq when the 117mSn in the femoral bone is assumed to be distributed uniformly in the bone matrix and the bone marrow is taken as the target region (Table 3). Whereas this theoretic value is not in good agreement with the experimentally determined value of 0.043 ± 0.002 cGy/kBq, distribution of the radioactivity in the endosteum as suggested by autoradiographic data (25) results in an even higher theoretic value. Therefore, unlike the theoretic results for 90Y-citrate, 32P-orthophosphate, and 33P-orthophosphate (20), our theoretic dosimetry model substantially overestimates the absorbed dose to the marrow from 117mSn(4+)DTPA. It is possible that a substantial fraction of the 117mSn resides on the periosteum, which would greatly impact the absorbed dose to the femoral marrow because of the nonpenetrating nature of the low-energy electrons emitted by this radionuclide.
The principal factor that limits the use of radiopharmaceuticals for reduction of bone pain is myelotoxicity. This limitation is largely associated with the high-energy β emitters that have been used to treat bone pain (e.g., 89Sr, 32P). The β particles emitted by these radionuclides irradiate not only sites associated with reduction of pain but also the bone marrow. Several investigators have advocated the use of low-energy (i.e., short range) β or CE emitters to reduce or eliminate myelotoxicity, and there is now a substantial amount of supporting clinical data (18,22,23,25,32,33). The ideal radiopharmaceutical would eliminate pain without causing deleterious effects to bone marrow or any other healthy tissue. To compare the relative efficacy of two radiopharmaceuticals to palliate bone pain, estimates of both the absorbed dose to the marrow and the absorbed dose to the target regions that are responsible for the pain relief are required. However, the mechanisms by which radiation provides pain relief are poorly understood (5). A host of different mechanisms have been advanced; however, none has been definitively established (34,35). Therefore, the target has not been clearly established.
Even though the target for alleviation of bone pain is not well defined, one can estimate the relative efficacy of different radiopharmaceuticals for this modality by considering the bone matrix as the target region (20). Assuming that the bone matrix is the target region and that the cumulated activity is integrated to infinity, D(matrix)/AInj = 1.07 cGy/kBq (Table 4). These data, in conjunction with the experimental mean absorbed dose to bone marrow per unit injected activity, can be used to examine the capacity of 117mSn(4+)DTPA to deliver a higher target-to-nontarget absorbed dose ratio than a given reference radiopharmaceutical. As previously defined, this can be quantified in terms of a relative advantage factor (RAF) with marrow serving as the nontarget region (20).
 Eq. 9If 32P-orthophosphate is taken as the reference radiochemical, the earlier results of Goddu et al. (20) can be used to calculate the RAF. Using the same models, they obtained a theoretic D(matrix)/AInj = 1.27 cGy/kBq and an experimental D(marrow)/AInj = 0.42 cGy/kBq for 32P-orthophosphate (20). Therefore, a comparison of 117mSn(4+)DTPA with 32P-orthophosphate yields an RAF of 8.2 (Table 5). A similar comparison between 33P- and 32P-orthophosphate yields an RAF of 4.2. If the theoretic marrow doses are used, then RAF values of 5.5 and 5.6 are obtained for 117mSn(4+)DTPA and 33P-orthophosphate, respectively (Table 5). Similar RAF values were obtained when a theoretic model of human cortical bone was used (33). This indicates that there is a substantial advantage for both 117mSn(4+)DTPA and 33P-orthophosphate over 32P-orthophosphate. Furthermore, the experimental data suggest that 117mSn(4+)DTPA is up to two times more advantageous than 33P-orthophosphate in this experimental model. The relatively low residence time for 117mSn(4+)DTPA in muscle compared with 33P-orthophosphate is an added asset of this radiopharmaceutical (Table 5). However, because of the longer physical half-life of 33P, the production and distribution of 33P-orthophosphate may be better suited for global distribution. It should also be pointed out that the theoretic calculations of Bouchet et al. (33) for human cortical bone suggest a substantial advantage for 117mSn and 33P over other radionuclides used to treat bone pain, such as 89Sr, 186Re, and 153Sm.
Eq. 9If 32P-orthophosphate is taken as the reference radiochemical, the earlier results of Goddu et al. (20) can be used to calculate the RAF. Using the same models, they obtained a theoretic D(matrix)/AInj = 1.27 cGy/kBq and an experimental D(marrow)/AInj = 0.42 cGy/kBq for 32P-orthophosphate (20). Therefore, a comparison of 117mSn(4+)DTPA with 32P-orthophosphate yields an RAF of 8.2 (Table 5). A similar comparison between 33P- and 32P-orthophosphate yields an RAF of 4.2. If the theoretic marrow doses are used, then RAF values of 5.5 and 5.6 are obtained for 117mSn(4+)DTPA and 33P-orthophosphate, respectively (Table 5). Similar RAF values were obtained when a theoretic model of human cortical bone was used (33). This indicates that there is a substantial advantage for both 117mSn(4+)DTPA and 33P-orthophosphate over 32P-orthophosphate. Furthermore, the experimental data suggest that 117mSn(4+)DTPA is up to two times more advantageous than 33P-orthophosphate in this experimental model. The relatively low residence time for 117mSn(4+)DTPA in muscle compared with 33P-orthophosphate is an added asset of this radiopharmaceutical (Table 5). However, because of the longer physical half-life of 33P, the production and distribution of 33P-orthophosphate may be better suited for global distribution. It should also be pointed out that the theoretic calculations of Bouchet et al. (33) for human cortical bone suggest a substantial advantage for 117mSn and 33P over other radionuclides used to treat bone pain, such as 89Sr, 186Re, and 153Sm.
The RAF values calculated above are based on experimental measurements and theoretic calculations for the normal bone of mice. There is ample evidence that uptake of radioactivity is generally much higher in diseased bone (1,12) with presumably little change in the marrow absorbed dose. Therefore, if the target for alleviation of bone pain were in the immediate vicinity of the metastases, the RAF values would be even higher than those calculated here (up to 8 for 117mSn compared with 32P). Regardless of the exact RAF values, the data for 117mSn presented here provide experimental support for the use of low-energy β and electron emitters in the palliation of bone pain (22,32).
CONCLUSION
The experimental and theoretic approaches used in this study support the use of the low-energy electron emitter 117mSn for alleviation of pain caused by metastatic disease in bone. This radionuclide offers a substantial therapeutic advantage over energetic β-particle emitters in that it has the potential to deliver high doses to bone while minimizing the absorbed dose to the bone marrow (17,18,22,32). Because of substantially reduced myelotoxicity, and an excellent safety profile (22,23,36,37), high-dose therapeutic administration of 117mSn(4+) chelates could be potentially useful for the treatment of primary or metastatic bone malignancies and early-stage metastatic disease in bone.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Diatide, Inc., for providing the 117mSn(4+)DTPA used in this study. This work was supported in part by U.S. Public Health Service grant CA-54891 and U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) grant DE-FG05–95ER62006. Work at Brookhaven National Laboratory was performed under U.S. DOE contract DE-AC02–98CH10886.
Footnotes
Received Dec. 28, 1999; revision accepted May 30, 2000.
For correspondence or reprints contact: Roger W. Howell, PhD, Department of Radiology, MSB F-451, UMDNJ–New Jersey Medical School, 185 S. Orange Ave., Newark, NJ 07103.











